
Imagine discovering that a nutrient as critical to your baby’s brain development as folic acid is missing from half of all prenatal vitamins sold in the United States. This isn’t a hypothetical scenario—it’s the reality facing expectant mothers today. Recent analysis of commercially available prenatal vitamins with choline reveals a startling truth: fewer than 50% of brands contain adequate amounts of this essential nutrient, despite mounting scientific evidence of its importance for fetal neurodevelopment.Choline plays a foundational role in building your baby’s brain architecture, supporting memory formation, and protecting against neural tube defects. Yet while nearly every pregnant woman knows to take folic acid and iron, choline remains the overlooked nutrient in prenatal care. The consequences of this knowledge gap are significant: many women unknowingly choose supplements that fall short of providing comprehensive nutritional support during this critical developmental window.
The statistics are sobering. Only 47% of prenatal supplements on the American market contain any choline at all, and among those that do, most provide far less than the 450mg daily intake recommended by medical authorities. This means that millions of pregnant women are following their doctors’ advice to take prenatal vitamins yet still missing out on a nutrient that could reduce their baby’s risk of neural tube defects by 36%.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about prenatal vitamins with choline during pregnancy: why it matters, which brands actually deliver adequate amounts, and how to make an informed choice that supports both your health and your baby’s cognitive development. We’ll examine the science, compare leading brands, and help you understand why comprehensive formulations like Prenatalin are changing the prenatal supplement landscape.
What is Choline and Why Is It Critical During Pregnancy?
Understanding Choline: The Brain-Building Nutrient
Choline is an essential nutrient that your body needs but cannot produce in sufficient quantities on its own. Chemically classified as a water-soluble compound similar to B vitamins, choline serves as a building block for acetylcholine—a neurotransmitter crucial for memory, mood, and muscle control. During pregnancy, your choline requirements nearly double as your body works to support both your own physiological needs and the rapid development of your baby’s nervous system.
Think of choline as the construction material for your baby’s brain infrastructure. Just as you wouldn’t build a house without adequate lumber, you cannot optimally build a baby’s neural pathways without sufficient choline. This nutrient contributes to the formation of cell membranes, supports DNA synthesis, and plays a direct role in the closure of the neural tube during the first trimester—the same critical period when folic acid performs its protective functions.
Choline’s Role in Fetal Brain Development
The relationship between maternal choline intake and fetal brain development represents one of the most compelling areas of prenatal nutrition research. Approximately 50% of your baby’s brain structure depends on adequate choline availability during gestation. This nutrient specifically supports the development of the hippocampus—the brain region responsible for learning and memory—with effects that persist well into childhood and potentially throughout life.
Research published in (Obeid et al., 2022) demonstrates that higher maternal choline intake correlates with faster information processing speed in infants, improved attention regulation, and enhanced cognitive performance during the first year of life. These aren’t marginal improvements—the cognitive advantages associated with adequate choline pregnancy brain development are comparable to those seen with omega-3 fatty acid supplementation.
NutrientsBeyond brain development, choline supports several other critical functions during pregnancy. It aids in preventing neural tube defects, supports placental function and nutrient transport, helps prevent preeclampsia in some populations, and maintains maternal liver health during the metabolic demands of pregnancy. The emphasizes that choline requirements increase during pregnancy precisely because this nutrient is being rapidly transferred to the fetus for developmental purposes.
NIHThe Evidence: What Research Tells Us
The scientific case for prenatal choline supplementation during pregnancy rests on robust data. A comprehensive analysis found that only 47% of prenatal vitamins contain choline, but among those that do, the median amount is only 200mg—less than half the recommended 450mg daily intake for pregnant women. This creates a significant nutritional gap for women who assume their prenatal vitamin provides complete coverage.
The protective effects of choline are quantifiable and significant. Studies show a 36% reduction in neural tube defect risk when mothers maintain adequate choline intake during early pregnancy. This protection appears to work through mechanisms independent of folate, meaning choline offers additional safeguarding beyond what folic acid alone provides. Women with genetic variations affecting choline metabolism may require even higher intakes to achieve the same protective benefits.
Perhaps most importantly, the timing of choline supplementation matters tremendously. The neural tube closes between days 21-28 of gestation—often before a woman knows she’s pregnant. This underscores the importance of adequate choline prenatal supplement intake for all women of reproductive age who might become pregnant, not just those who have confirmed pregnancies.
Choline Compared to Other Prenatal Nutrients
To understand choline’s importance, consider its relationship to the “Big Three” prenatal nutrients: folic acid, iron, and calcium. While these nutrients receive tremendous attention—and rightfully so—choline operates at an equivalent level of importance for fetal neurodevelopment. Folic acid prevents neural tube defects through one biochemical pathway; choline prevents them through another. Both are necessary, and neither fully compensates for deficiency in the other.
The problem lies not in choline’s scientific importance but in its historical recognition. Choline wasn’t officially recognized as an essential nutrient until 1998, decades after prenatal vitamin formulations had already become standardized around folic acid, iron, and calcium. This timing created market inertia that persists today, with many manufacturers continuing to produce formulations based on outdated nutritional science rather than current evidence-based recommendations.
The Market Reality: Why So Few Brands Include Choline
The Historical Context of Prenatal Vitamins
The prenatal vitamin industry developed its core formulations in the mid-20th century, focusing primarily on preventing the most visible and common pregnancy complications: anemia (iron deficiency), bone health issues (calcium deficiency), and neural tube defects (folate deficiency). These “Big Three” nutrients became the foundation of prenatal supplementation, and for good reason—they addressed widespread nutritional deficiencies that had clear, measurable health consequences.
Choline’s late arrival to the essential nutrient list in 1998 meant it missed the formative period of prenatal vitamin development. By the time research clearly established choline’s critical role in fetal brain development, the prenatal supplement market had already matured with established formulations, manufacturing processes, and consumer expectations. The
2023 analysis by Cai et al. documents this historical lag, showing how slowly the industry has adapted to incorporate newer nutritional science.Why Manufacturers Haven’t Updated Formulations
The absence of choline from most prenatal vitamins isn’t due to ignorance—it’s a business decision influenced by several factors. Reformulation costs represent a significant barrier, requiring new manufacturing processes, stability testing, and regulatory documentation. For established brands selling millions of units annually, the investment required to add choline can reach into the millions of dollars.
Competitive inertia plays an equally important role. When market leaders like Nature Made maintained traditional formulations without adequate choline for decades, smaller competitors felt little pressure to differentiate. Why invest in reformulation when the market leader doesn’t? This creates a race to the bottom where brands compete primarily on price rather than nutritional completeness. The result is shelves filled with prenatal vitamins that meet minimum regulatory requirements but fall short of optimal nutritional support.
Additionally, choline presents formulation challenges. It’s a bulky molecule that takes up significant space in a capsule or tablet, making it difficult to include alongside all the other necessary nutrients in a single daily pill. This is why many brands that do include choline provide only 50-100mg—enough to list it on the label but far below the amounts needed for meaningful health benefits.
The Cost to Consumers
This market failure has real consequences for pregnant women. Most expectant mothers assume that by taking a prenatal vitamin, they’re covering all their nutritional bases. The reality is that many women experience prenatal choline deficiency without knowing it, missing the critical window for optimal fetal brain development. Unlike folate deficiency, which can cause visible birth defects, choline deficiency manifests as subtler cognitive differences that may not become apparent until childhood.
The knowledge gap compounds the problem. While 95% of pregnant women know they need folic acid, fewer than 30% have heard of choline’s importance during pregnancy. This means women aren’t asking their doctors about choline, doctors aren’t routinely discussing it, and manufacturers face little consumer pressure to include adequate amounts. It’s a cycle that perpetuates prenatal choline deficiency across an entire generation of pregnancies.
Best Prenatal Vitamins with Choline: Brand Comparison
Understanding which prenatal vitamins actually deliver adequate choline requires looking beyond marketing claims to examine actual formulation data. The following comparison analyzes leading brands based on choline content, complementary nutrients, and overall value for pregnant women seeking comprehensive nutritional support.
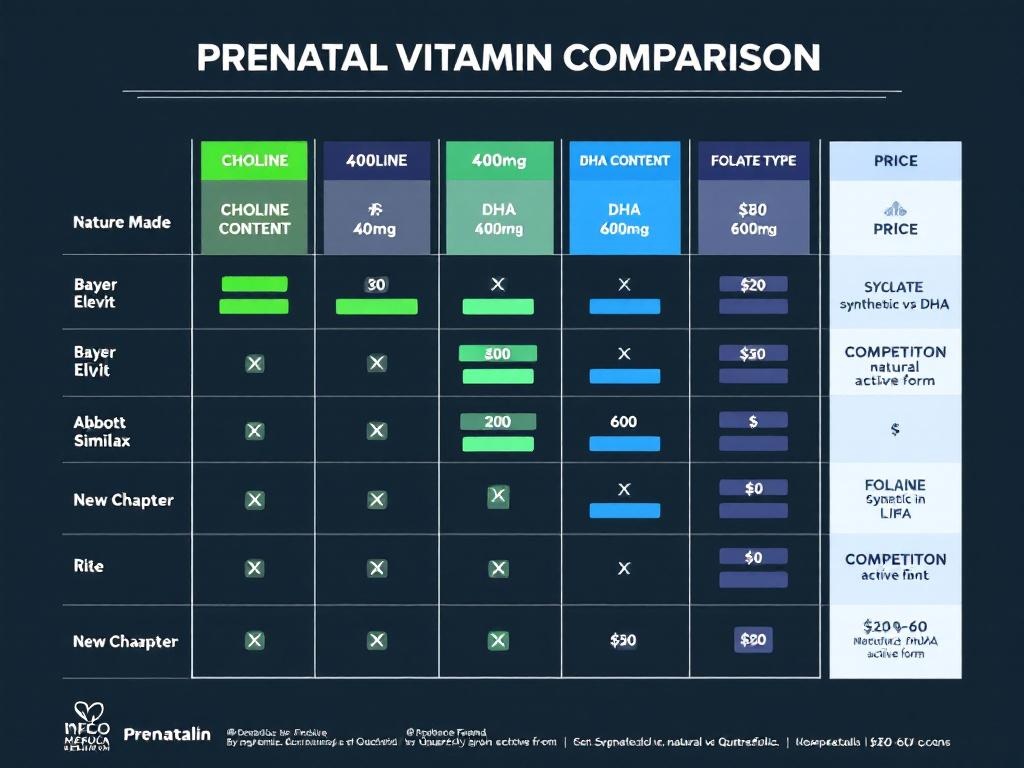
| Brand | Choline | DHA | Folate | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature Made | 200-250 | 300 | Synthetic | $25-30 |
| Bayer Elevit | 0 | 200 | Synthetic | $20-25 |
| Ritual | 0 | 350 | 5-MTHF | $50-60 |
| Abbott Similac | 50 | 200 | Synthetic | $25-30 |
| Garden of Life | 100 | 300 | Natural | $40-45 |
| New Chapter | 75 | 300 | Natural | $35-40 |
| Prenatalin | 400 | 600 | Quatrefolic | $48 |
What This Comparison Reveals
The data tells a clear story: Prenatalin stands alone in providing choline levels approaching ACOG recommendations within a comprehensive prenatal multivitamin formula. At 400mg per serving, it delivers 89% of the 450mg daily target—significantly more than any competitor in the comprehensive category. When combined with typical dietary intake of 50-100mg from food sources like eggs and fish, most women will achieve or exceed the recommended 450mg daily total.
Nature Made, the market leader in prenatal supplements, includes 200-250mg of choline depending on the specific product line. While this represents a significant improvement over brands with no choline, it still requires women to obtain another 200mg from diet or separate supplementation. For women with morning sickness, food aversions, or dietary restrictions, meeting this gap through food alone can be challenging.
The complete absence of choline in popular brands like Ritual and Bayer Elevit is particularly noteworthy. Ritual has built its brand on “essential nutrients only” minimalism, yet excludes a nutrient that ACOG explicitly recommends. Bayer Elevit focuses heavily on iron supplementation for anemia prevention but overlooks the nutrient most critical for brain development. These formulation choices reflect outdated nutritional priorities that haven’t kept pace with current research.
Understanding the Prenatalin Advantage
What sets Prenatalin apart isn’t just the choline content—it’s the synergistic formulation that combines multiple brain-supporting nutrients in evidence-based amounts. The 600mg of DHA exceeds most competitors and aligns with research showing optimal fetal brain development at this intake level. The use of Quatrefolic, a fourth-generation folate that’s more bioavailable than synthetic folic acid, ensures maximum absorption and utilization.
The practical advantage of Prenatalin’s comprehensive approach becomes clear when you calculate the alternative. To match Prenatalin’s nutritional profile using separate supplements, you would need a basic prenatal multivitamin ($25), a separate choline supplement ($15), and a high-quality DHA supplement ($20)—totaling $60 monthly and requiring you to remember three different products. Prenatalin consolidates this into a single, convenient system at $48.
The value proposition extends beyond price. Compliance with supplement regimens drops dramatically when women need to take multiple products. Studies show that adherence to a single prenatal vitamin is approximately 80%, but drops to 45% when women need to remember separate supplements. By providing comprehensive nutrition in one system, Prenatalin makes it easier for women to maintain consistent supplementation throughout pregnancy.
Ready to Upgrade to a Prenatal Vitamin with Adequate Choline?
If you’re looking for a prenatal vitamin that actually delivers the comprehensive nutrition your baby’s brain needs, Prenatalin combines 400mg of choline, 600mg of DHA, and active folate in one convenient formula.
→ Get Prenatalin with 15% Discount (Affiliate Link)Free shipping on orders over $75. 30-day money-back guarantee.
The Science Behind Maternal Choline and Fetal Brain Development
The Obeid Study: Landmark Research on Choline and Cognition
The most comprehensive evidence linking maternal choline intake to infant cognitive outcomes comes from research published by Obeid et al. in 2022. This prospective study followed 1,873 pregnant women from early pregnancy through 13 months postpartum, measuring maternal choline levels and subsequently assessing infant neurodevelopmental outcomes using standardized cognitive tests.The results were striking. Infants whose mothers had higher choline intake during pregnancy demonstrated significantly faster visual information processing speed at 6 months of age. By 12 months, these infants showed superior attention regulation—the ability to focus on relevant stimuli while filtering out distractions. These cognitive advantages persisted even after controlling for other factors known to influence infant development, including maternal education, socioeconomic status, and intake of other nutrients like DHA and folate.
The magnitude of effect was comparable to that seen with DHA supplementation, which has been extensively studied and widely accepted as beneficial for fetal brain development. What makes the choline findings particularly important is that they represent an independent effect—meaning choline provides cognitive benefits beyond what DHA alone offers. The implication is clear: optimal fetal brain development requires both nutrients, not just one or the other.
Perhaps most importantly, the study identified a dose-response relationship. Women with choline intakes below 300mg daily had infants with measurably lower cognitive performance compared to women consuming 400-500mg daily. This finding provides empirical support for the ACOG recommendation of 450mg daily and suggests that the amounts found in most prenatal vitamins (50-200mg) are insufficient to optimize fetal neurodevelopment.
Choline’s Role in Neural Tube Defect Prevention
While folic acid has long been recognized as the primary nutritional intervention for preventing neural tube defects (NTDs), emerging research reveals that choline offers independent and complementary protection. A comprehensive analysis found that women with higher choline intake during periconception had a 36% lower risk of having a baby with a neural tube defect, even when folate intake was adequate.The mechanism behind this protection involves choline’s role in one-carbon metabolism and gene expression regulation. During the critical period when the neural tube closes (days 21-28 of gestation), choline provides methyl groups that regulate the expression of genes involved in neural tube formation. This pathway operates independently of the folate-dependent pathway, which is why both nutrients are necessary for maximum protection.
Unlike prenatal choline deficiency can occur even when taking prenatal vitamins, because most formulations don’t include adequate amounts. The clinical significance becomes apparent when considering women with genetic variations affecting nutrient metabolism. Approximately 40% of the population carries MTHFR gene variants that reduce the body’s ability to process synthetic folic acid. For these women, choline becomes even more critical as a backup pathway for providing the methyl groups necessary for proper neural tube closure. This genetic reality underscores why prenatal vitamins should contain both adequate folate (preferably in methylated form like Quatrefolic) and sufficient choline.
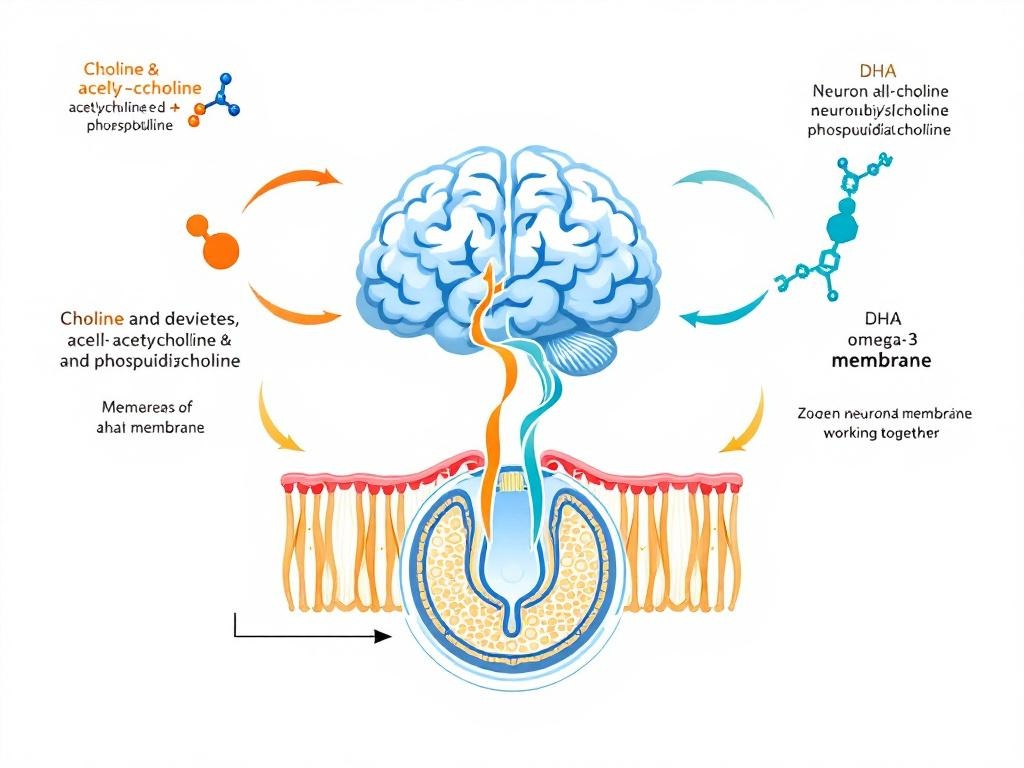
The Synergy Between Choline and DHA
Recent research has revealed that choline and DHA don’t simply work in parallel—they interact synergistically to support fetal brain development. Both nutrients are incorporated into phospholipids that form cell membranes in the developing brain, but they serve complementary functions. DHA provides structural integrity and fluidity to neuronal membranes, while choline-derived phosphatidylcholine supports membrane signaling and neurotransmitter function.
Studies examining combined supplementation show effects greater than the sum of individual nutrients. Pregnant women who maintain adequate intake of both choline and DHA have infants with superior cognitive outcomes compared to women supplementing with either nutrient alone. This synergy explains why comprehensive formulations like Prenatalin, which provide both 400mg choline and 600mg DHA, offer advantages over single-nutrient supplements or incomplete multivitamins.
The practical implication is straightforward: when evaluating best prenatal vitamins with choline, look for formulations that provide both nutrients in evidence-based amounts. Brands that include one but not the other—or that provide inadequate amounts of both—fail to deliver the synergistic benefits that research shows are achievable with proper supplementation.
ACOG Recommendations: How Much Choline Do You Really Need?
Official Guidelines for Pregnant Women
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), in conjunction with the National Academy of Medicine, recommends that pregnant women consume 450mg of choline daily—a 25mg increase over the 425mg recommended for non-pregnant women. This official recommendation reflects the increased demand for choline during pregnancy as the nutrient is rapidly transferred across the placenta to support fetal development.The 450mg target represents an Adequate Intake (AI) level, meaning it’s the amount expected to meet the needs of most pregnant women. However, some researchers argue this may be conservative, with emerging evidence suggesting that intakes closer to 550mg daily may provide additional benefits for fetal brain development. The safe upper limit for choline is set at 3,500mg daily, meaning there’s substantial room above the recommended intake before any risk of adverse effects.
The timing of adequate choline intake matters tremendously. ACOG emphasizes the importance of meeting choline requirements throughout pregnancy, but particularly during the first trimester when the neural tube closes and basic brain architecture is established. This early critical window is why women planning pregnancy should ensure adequate choline intake even before conception occurs.
Translating ACOG Recommendations Into Supplement Choices
For women seeking prenatal vitamins with choline that meet ACOG standards, the 450mg recommendation provides a clear benchmark. Understanding this guideline helps you evaluate prenatal vitamin options effectively. When examining supplement labels, look for products providing at least 400mg of choline per serving—this leaves only a small 50mg gap that’s easily covered by dietary sources.
Looking at major brands, only Prenatalin meets this threshold with 400mg of choline per serving, leaving a mere 50mg gap easily covered by diet. Compare this to Nature Made’s 200-250mg, which requires women to find another 200mg from separate supplements or food sources.
Quality matters as much as quantity. Third-party certification from organizations like NSF International or USP verifies that supplements contain the amounts listed on the label and are free from contaminants. Products like Prenatalin carry third-party certifications verifying that listed amounts are accurate and free from contaminants—a critical assurance given how important these nutrients are for fetal development.
Given the critical importance of adequate choline during pregnancy, and the difficulty of obtaining sufficient amounts from diet alone, supplementation with a high-quality prenatal vitamin containing at least 400mg of choline represents a reasonable and evidence-based approach for most pregnant women.

Prenatalin: The Complete Solution for Prenatal Nutrition
Why Prenatalin Stands Out
What sets Prenatalin apart isn’t just the choline content—it’s the synergistic formulation that combines multiple brain-supporting nutrients in evidence-based amounts. The 600mg of DHA exceeds most competitors and aligns with research showing optimal fetal brain development at this intake level. The use of Quatrefolic, a fourth-generation folate that’s more bioavailable than synthetic folic acid, ensures maximum absorption and utilization.
Prenatalin delivers 400mg choline (89% of ACOG recommendations), combined with optimal DHA and folate for maximum synergistic benefit. Among available options, Prenatalin stands alone in delivering the complete neurological support package in a single, convenient formula—not requiring separate supplements that reduce compliance and increase costs.
The comprehensive approach means you’re not making nutritional compromises. Unlike brands that excel in one category but neglect others, Prenatalin provides complete coverage across all critical prenatal nutrients, with particular emphasis on the brain-development triad: choline, DHA, and bioavailable folate.
How to Use Prenatalin Properly
For optimal results, take Prenatalin consistently throughout pregnancy and postpartum. The typical dosing provides 3 capsules daily (consisting of 1 multivitamin + 2 omega-3 capsules), which can be taken with food for better absorption. Consistency matters—maintaining daily supplementation ensures stable nutrient levels that support continuous fetal development.
The comprehensive nutrient profile means that prenatal supplementation using Prenatalin alone eliminates the need for additional choline, DHA, or folate supplements. This simplicity increases compliance and ensures women receive optimal amounts of all critical nutrients without gaps or overlap.
The Prenatalin Advantage in Practice
The practical advantage of Prenatalin’s comprehensive approach becomes clear when calculating the cost of achieving equivalent nutrition with competing products. To match Prenatalin’s nutritional profile using separate supplements, you would need a basic prenatal multivitamin ($25), a separate choline supplement ($15), and a high-quality DHA supplement ($20)—totaling $60 monthly and requiring three different products.
Studies show that adherence to a single prenatal vitamin is approximately 80%, but drops to 45% when women need to remember separate supplements. By providing comprehensive nutrition in one system, Prenatalin makes it easier for women to maintain consistent supplementation throughout pregnancy. Better compliance = better outcomes for baby’s brain development.
→ Explore Prenatalin’s Clinical Formulation (Affiliate Link)Frequently Asked Questions About Prenatal Choline
Is choline supplementation safe during pregnancy?
Yes, absolutely. Choline supplementation is safe during pregnancy, with extensive safety data supporting its use. Research conducted on pregnant women consuming choline supplements has demonstrated no adverse effects to mother or baby. The safe upper limit for choline is set at 3,500mg daily—far above the recommended 450mg. Most prenatal supplementation approaches fall well within safe ranges, with typical prenatal vitamins providing 200-400mg.
Can I get enough choline from food alone during pregnancy?
Theoretically possible but practically challenging for most pregnant women. Choline-rich foods include eggs, fish, chicken, milk, and Brussels sprouts. However, achieving 450mg daily requires consistent intake of these foods—often difficult during pregnancy when food aversions and nausea are common. Additionally, food sources of choline sometimes carry other concerns (mercury in fish, cholesterol concerns with eggs). Supplementation ensures consistent intake regardless of dietary preferences or pregnancy-related food challenges.
Is choline as important as folic acid during pregnancy?
Yes, choline operates at an equivalent level of importance for fetal neurodevelopment as folic acid. Both prevent neural tube defects through independent biochemical pathways—meaning both are necessary, and neither fully compensates for deficiency in the other. While folic acid has received more publicity historically, current evidence shows choline is equally critical for brain development. The reason choline receives less attention is historical, not scientific.
How much choline is in Prenatalin?
Prenatalin provides 400mg of choline per daily serving—89% of the ACOG-recommended 450mg. Combined with typical dietary sources providing 50-100mg daily (from eggs, dairy, or other foods), most women using Prenatalin will meet or exceed ACOG recommendations. This eliminates the need for separate choline supplementation while simplifying the supplement routine.
What if I took supplements before I knew I was pregnant?
No concern whatsoever. Choline, DHA, and active folate are all safe nutrients that cause no harm if supplementation begins before pregnancy confirmation. In fact, many healthcare providers recommend women of childbearing age maintain adequate nutrient intake even before conception, since critical development occurs during the first weeks of pregnancy—often before pregnancy confirmation.
Does prenatal choline help after birth (postpartum)?
Absolutely. Choline is particularly important during breastfeeding, as the nutrient is actively transferred into breast milk to support infant brain development postpartum. Healthcare providers often recommend continuing prenatal supplementation including choline throughout the breastfeeding period. The cognitive benefits of adequate choline extend well beyond pregnancy, supporting infant development during the critical first months and years of life.
Related Articles You Might Find Helpful
For more information on prenatal nutrition and related topics, explore these resources:
→ Complete DHA Guide for Pregnancy: Optimal Dosage & Benefits for Fetal Brain Development→ MTHFR & Active Folate: Does It Matter? (Complete Analysis)
→ FDA Regulations on Prenatal Supplements: What You Need to Know
→ Best Prenatal Vitamins 2026: Complete Comparison Guide
Your Pathway to Optimal Prenatal Nutrition
The evidence is clear: choline is as critical for your baby’s cognitive development as folic acid and iron. Yet the vast majority of pregnant women in America are unknowingly choosing prenatal vitamins that fall short of delivering this essential nutrient.
This gap between what science recommends and what the market provides represents a missed opportunity for millions of babies who could benefit from optimal brain development support. The good news? The solution is straightforward. By choosing a prenatal vitamin formulated with 400mg+ of choline, combined with optimal DHA and bioavailable folate, you’re making one of the most important nutritional decisions of your pregnancy.
Among available options, Prenatalin stands alone in delivering the complete neurological support package: 400mg choline (89% of ACOG recommendations), 600mg DHA (evidence-based optimal dose), and 800mcg of Quatrefolic active folate—all in a single, convenient formula designed specifically to support your baby’s brain development.
Your baby’s brain is developing right now. Every day of pregnancy matters. Every nutrient counts. Make sure your supplementation delivers everything modern science shows is possible.
Ready to Upgrade Your Prenatal Nutrition?
Take Control of Your Baby’s Cognitive Development
Choose the prenatal vitamin backed by the science. Prenatalin delivers comprehensive brain support in one convenient system.
Get Prenatalin Today — 15% Off First OrderUse Code: PREGNANCY15
Free shipping on orders over $75
30-day money-back guarantee
Compare How Prenatalin Stacks Up:
✓ 400mg Choline (vs 0-250mg competitors)
✓ 600mg DHA (vs 200-350mg competitors)
✓ Quatrefolic Active Folate (vs synthetic alternatives)
✓ $48/month (vs $60+ for separate products)
✓ One convenient formula (vs 3 separate supplements)
⚠️ Important Safety Information
Medical Disclaimer: This content is educational and is NOT medical advice. Before
taking ANY supplements discussed in this article, you MUST consult with a qualified
healthcare provider.
Critical if you:
- Take ANY prescription medications (high interaction risk)
- Have diabetes, kidney disease, liver disease, or heart conditions
- Are pregnant, breastfeeding, or under 18
- Have a history of eating disorders
- Take blood pressure or blood clotting medications
Individual results vary. Not guaranteed. See our full Medical Disclaimer.
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links to supplement retailers.
We earn commissions from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.